 Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a serious mental illness that causes unusual shifts in mood. Ranging from extreme high (mania) to low depression. Bipolar disorder is disabling and severe psychiatric disorders commonly perceived as equally affecting both men and women. But rapid cycling is seen more often in women. Women also tend to experience more depressive and mixed state episode than do men.
Types of Bipolar Disorder:
The categories include:
Bipolar 1 Disorder:
Involve manic episode lasting 7 days or more or severe mania that requires hospitalization.
Person experience major depressive episode that last 2 weeks or more.
Bipolar 2 Disorders:
Both mania and depression but mania is less severe than in bipolar 1 called a (hypomania).
Cyclothymic:
Also known as cyclothymic includes symptoms of hypomania and depression that last for 2 year or more in adult or 1 year in children.
Other Type:
People with their disorder experience symptoms that do not fall into the above categories. These symptoms may stem from drug or alcohol use or some other medical condition.
Symptoms- Bipolar Disorder:
Depression:
During a period of depression, your symptoms may include:
- Feeling sad, hopeless or irritable most of the time.
- Lacking energy
- Difficulty concentrating and remembering things.
- Self-doubt
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Suicidal thoughts
Manic:
The manic phase of bipolar disorder may include:
- Feeling very happy
- Talking very quickly
- Feeling self-important
- Easily irritated
- Hallucination and illogical thinking
- Making decision or saying things that are out of character and that other see as being risky or harmful.
Pattern of depression and mania:
A person, who has bipolar disorder, may have episode of depression more regularly than episode of mania, or vice versa.
Between episode of depression and mania a person may sometimes have periods where he/she have a ‘normal’ mood.
But the pattern is not always the same for example
Rapid Cycling:
Where a person with bipolar disorder repeatedly swings from a high to low phase quickly without having a ‘normal’ period in between.
Mixed State:
Where a person with bipolar disorder experience symptoms of depression and mania together; for example, over activity with a depress mood.
Cyclothymic:
If person mood swing last a long time but are not a severe enough to be classed as bipolar disorder, a person may be diagnosed with mild form bipolar disorder called cyclothymic.
Bipolar in Pakistan:
The estimates rate of prevalence for bipolar spectrum disorder among students of Pakistan is 14.3%. No significant difference in prevalence of BSD was observed in either gender. However, the age group of 20-21 year was the most affected one. Lots of myths in country like Pakistan people think that someone had done some sort of ‘Black magic’ on person. But in reality it’s a mental illness.
Bipolar in women:
Bipolar effective disorder in women is a challenging disorder to treat. It is unique in its presentation in women and characterized by later age of onset, seasonality, atypical presentation, and a higher degree of mixed episodes. Medical and psychiatric co-morbidity adversely affects recovery from the bipolar disorder (BD) more often in women. Co-morbidity, particularly thyroid disease, migraine, obesity, and anxiety disorders occur more frequently in women while substance use disorders are more common in men. Treatment of women during pregnancy and lactation is challenging. Pregnancy neither protects nor exacerbates BD, and many women require continuation of medication during the pregnancy. The postpartum period is a time of high risk for onset and recurrence of BD in women. Prophylaxis with mood stabilizers might be needed. Individualized risk/benefits assessments of pregnant and postpartum women with BD are required to promote the health of the women and to avoid or limit exposure of the foetus or infant to potential adverse effects of medication.
Female patients of BD are more likely to report history of sexual abuse, which is associated with a worse course of this disorder, earlier age of onset, greater co-morbidity and a higher rate of suicidal.
Bipolar disorder different from schizophrenia and psychotic condition:
Bipolar disorder and schizophrenia are psychiatric conditions that have some common traits, but also key differences. Bipolar disorder causes shifts in mood, energy levels, and thinking. Schizophrenia causes a person to appear to lose touch with reality.
People with bipolar disorder may experience episodes of mania and depression, often separated by periods of relative stability.
Individuals with schizophrenia experience symptoms of psychosis, such as hallucinations or delusions. Some people with bipolar disorder also experience psychotic symptoms. Because of some overlap in symptoms, getting the right diagnosis can be challenging. Also, a person can have both Trusted Source schizophrenia and bipolar disorder, which can complicate diagnosis.
Some people have schizoaffective disorder, which involves a combination of schizophrenia symptoms and those of a mood disorder.
Bipolar disorder and relationships:
Particularly with a partner who has been diagnosed with bipolar disorder: Feeling that you’re a caretaker in the relationship
Experiencing burnout
Sacrificing your life goals, values, and needs to be with your partner
Your partner stopping their treatments or medication could also be a cautionary sign for the future of the relationship. Also, as with any relationship, you should never feel that your partner is putting either you or themselves in danger.
Unhealthy signs go both ways. A person diagnosed with bipolar disorder may see red flags from their partner, too.
“A partner who is stigmatizing and very negative about mental health issues, which is unfortunately fairly common
Bipolar and drug addiction:
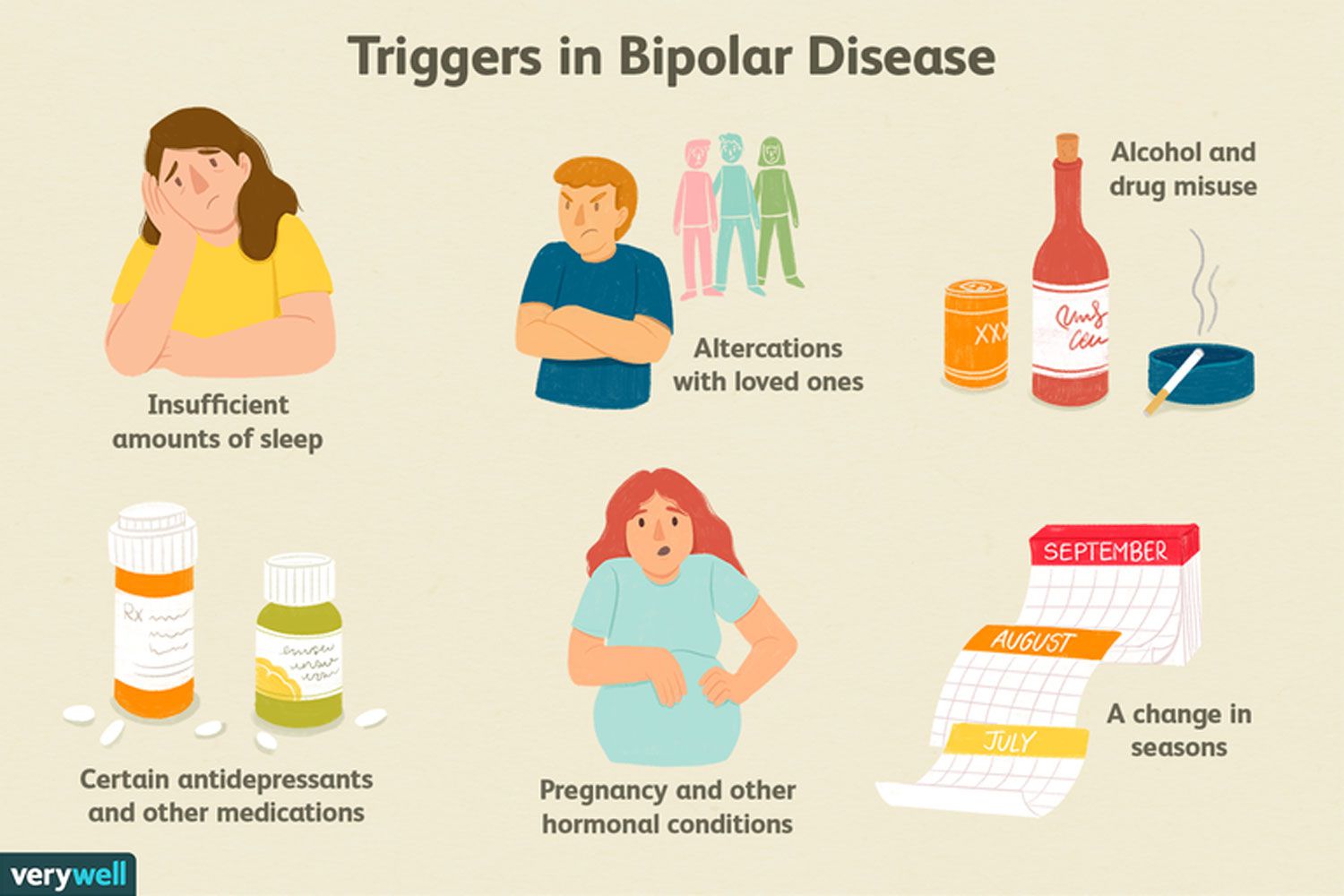
Compared to the general population, people with bipolar disorder are more likely to be addicted to drugs and alcohol. In some studies, about 60% of participants with bipolar disorder had some history of substance abuse. Unfortunately, it’s not known why bipolar disorder makes people more likely to abuse drugs.
Frequent drug and alcohol use can cause physical changes in the brain. The most apparent change happens to the brain’s reward system, making using drugs more pleasurable and triggering drug-seeking behaviour. People with bipolar disorder may experience manic or depressive episodes. When they are in a manic phase, they may abuse stimulants like cocaine to extend this high-energy state. Or, when they’re in a depressive state, they may reach for sedatives or depressants to calm feelings of hopelessness.
In some cases, it could be said that substance abuse caused bipolar disorder. However, substance abuse can trigger various mental health disorders, including anxiety, depression, and schizophrenia. Nonetheless, when talking about drug-induced bipolar disorder, it’s referring to someone who was previously healthy and developed a mental illness after abusing drugs.
World bipolar disorder day 30 march each year.
Treatment at New Hope:
In new hope rehab centre healthcare providers will suggest a treatment plan based on the person’s symptoms. The new hope team carefully plan a treatment. A psychiatrist and physician plan a medication and a skillful psychologist provide psychotherapy.
Psychotherapy can be important treatment component for people with bipolar disorder. It can enable them to recognize changes in thoughts and mood and respond accordingly. Lifestyle modification is also important key in the treatment of bipolar.
Our New Hope team aim is to provide awareness regarding mental health general and specifically bipolar and other mental health disorders.
About the author:
Aleena Safdar : Clinical Psychologist at New Hope Rehab and caring centre.
She can be reached at: aleena safdar 230@gmail.com